HAIR TRANSPLANT
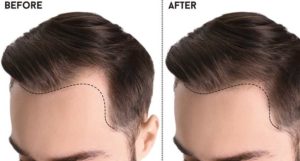
HAIR TRANSPLANT
Hair transplantation is a surgical technique in which individual hair follicles are transferred from one part of the body (the donor site) to the bald or balding part (the recipient site). It is mainly used to treat male pattern hair loss, whereby grafts containing hair follicles that are genetically resistant to hair loss are transplanted onto the balding scalp. However, it is also used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, and pubic hair, and to fill in scars resulting from accidents or surgical procedures such as face lifts and face lifts from previous hair transplants. Hair transplantation differs from skin transplantation in that the grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis surrounding the hair follicle and many small grafts are transplanted instead of a single strip of skin.
Modern hair transplantation allows you to achieve a natural look by imitating natural hair. This hair transplant procedure is called Follicular Unit Transplant (FUT). Donor hair can be obtained in two very different ways:
1. Strip Harvesting – A strip of scalp is removed under local anesthesia, then the wound is stitched and a piece of scalp tissue is cut into small pieces of tissue called grafts, which are then transplanted into the patient’s thinned area. Head. This method leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which must be covered by the patient’s hair (if it is long). The recovery period lasts about two weeks and requires medical staff to remove the stitches.
2. Extraction of Follicular Units or FUE Harvest: Individual hair follicles are harvested under local anesthesia; This type of micro-threading uses small punches whose diameter varies between 0.6 mm and 1.25 mm. Then each follicle is reinserted into the scalp with a micro blade in the sparse area. Because the hair follicles are individual and little tissue is removed, there is no visible scarring or postoperative pain, and no sutures need to be removed. Recovery from FUE occurs within 7 days.
Thanks to the latest surgical advances, recovery time is immediate. No bed rest or hospitalization is required after hair transplantation and the patient can go home immediately after the OPD procedure. You can also return to the practice from the 2nd day after the operation (provided the hair transplant is performed by a licensed and qualified/experienced surgeon).Thanks to these experienced surgeons, the procedure is almost painless, whereas it used to be associated with great pain.
Procedures
At the first visit, the surgeon analyzes the patient’s scalp, discusses their preferences and expectations, and recommends the best approach (e.g., one or more sessions) and the results that can reasonably be expected.
Operations
Transplant surgeries are performed on an outpatient basis under light sedation (optional) and injectable local anesthesia and typically last about four hours. Before the donor scalp is removed, it is washed with shampoo and then treated with an antibacterial chemical.
In normal follicular surgery, the surgeon removes a strip of skin from the back of the head where hair grows well. The trimmed strip measures approximately 1-1.5cm x 15-30cm. After closing the resulting wound, the assistants begin excising individual follicular grafts from the strip. Using binocular stereomicroscopes, they carefully remove excess fibrous and fatty tissue, trying to avoid damaging the follicular cells used for transplantation. The last closure method is called “trichophytic closure” and results in a much finer scarring in the donor area.
The FUE
harvest eliminates the need to harvest large areas of scalp tissue and can produce very natural looking results when used by the experienced surgeon.
The surgeon then uses very small micro blades or fine needles to puncture the graft sites, placing them in a specific density and pattern, and positioning the wounds at a fixed angle to create a realistic hair pattern. The last part of the procedure is usually done by the assistants, who place the individual grafts.
Aftercare
Advances in wound care allow the use of semi-permeable dressings that allow for the application and exchange of blood and tissue fluids at least once a day. Shampooing starts two days after the operation. Some surgeons wash the patient with shampoo the day after the operation. Shampooing is important to prevent crusting around the hair shaft. The scab adheres to the hair shaft and increases the risk of losing the newly transplanted hair follicles in the first 7-10 days after surgery.
In the first ten days, virtually all transplanted hairs will inevitably fall out (“shock loss”) after the trauma of transference. After two to three months, new hair begins to grow from the displaced follicles. The patient’s hair grows normally and will continue to grow thicker over the next six to nine months. Subsequent hair loss is likely to only affect the untreated areas. Some patients choose to take medication to delay this loss, while others plan a subsequent transplant to address this possibility.
Modern techniques
There are different hair follicle removal techniques, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Regardless of the donor collection technique, the correct collection of the hair follicles is essential to ensure the vitality of the transplanted hair and to avoid shearing, i.e. cutting the hair shaft from the hair follicle. Hair follicles grow at a slight angle to the skin’s surface, which means that regardless of the transplant technique, the tissue must be taken at right angles and not perpendicular to the surface.
Currently, there are three main methods of obtaining donor grafts: strip harvesting, follicular unit extraction, and direct hair implantation.
The strip sampling is the most common technique for collecting hair and hair follicles at the sampling site, most commonly at the back of the head and sides of the scalp. A scalpel with one, two or three blades is used to remove strands of hair at the donor site. Each incision is carefully planned to ensure the hair follicles are removed intact. After removal, the strip is divided into follicular units, which are small, naturally formed clusters of hair follicles.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is performed in one long session. According to the literature 98, with careful technique there is no reason to fear graft transplantation. The possible rate of live transplant results is 7%. It is believed that not all hair transplant candidates are suitable for FUE hair transplant. A test called the Fox test is currently performed before surgery to determine the suitability of donor tissue available for transplantation.
Side Effects
Hair loss, also called “shock loss,” is a common side effect that is usually temporary. Hair loss is also common, with fifty to a hundred hairs falling out every day.
Other side effects include swelling of areas like the scalp and forehead. If it becomes uncomfortable, medication can reduce the swelling. Also, the patient should be careful when the scalp begins to itch, as scratching aggravates the condition and causes scabs. To relieve itching, you can use a moisturizer or massage shampoo.
A few years after the operation, there may be more hair loss and the transplanted areas remain in place. This results in odd strands of hair unless they are removed or more hair is transplanted.

